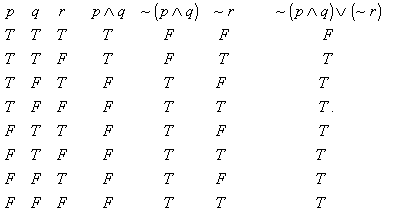Discrete Mathematics
Logic
Logic is a proper or reasonable way of thinking about or understanding something, and the science that studies the formal processes used in thinking and reasoning
Overview:
You can't get very far in logic without talking about propositional logic also known as propositional calculus.
A proposition is a declaritive sentence (a sentence that declares a fact) that is either true or false.
Examples of propositions:
- Tallahassee is the capital of Florida
- Washington D.C. is not the capital of the United States
- 0 + 2 = 2
- 2 + 3 = 10
Propositions 1 and 3 are true, while propositions 2 and 4 are false, not both.
We use letters to denote propositional variables, similar to how letters can represent numbers. The conventional letters used are p,q,r,s,..... The truth value of a proposition is denoted by T and false value by F.
Logical Equivalences Using Laws
randerson112358Prove the following logical equivalence using laws of logical equivalence, and without using a truth table.
Download PDFTautology:
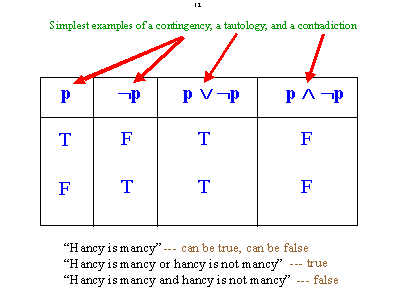
In logic, a tautology (from the Greek word ταυτολογία) is a formula that is true in every possible interpretation. Philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein first applied the term to redundancies of propositional logic in 1921.
Logical Equivalences Tautology
randerson112358Use the laws of logic to show that the following logical expression is a tautology without the truth table:
Download PDFContradiction:
In logic, a A contradiction is a proposition that is always false. The opposite of a tautology.
Logical Equivalences Contradiction
randerson112358Use the laws of logical equivalence to show the following proposition is a contradiction.
Truth Table Description
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, boolean functions, and propositional calculus—to compute the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is, on each combination of values taken by their logical variables (Enderton, 2001). In particular, truth tables can be used to tell whether a propositional expression is true for all legitimate input values, that is, logically valid.
Code:
class AndOrDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int p=1;// p = True represented by the number 1
int q= 0;// q = False represented by the number 0
char BOOLEAN;
char TRUE = 'T';
char FALSE = 'F';
// This represents p and q
if(p && q){
BOOLEAN = TRUE; //The code will not go here
}
else{
BOOLEAN = FALSE; //The code will go here
}
System.out.println("Boolean value = " + BOOLEAN);
//This represents p or q
if(p || q){
BOOLEAN = TRUE; //The code will go here
}
else{
BOOLEAN = FALSE; //The code will NOT go here
}
System.out.println("Boolean value = " + BOOLEAN);
}
}